Volume 77 • Number 4 • December 2016
Chair's Message
Editor's Message
Research
Purpose: The objective of this study was to investigate factors affecting the intention of Registered Dietitians (RDs) to discuss nutrigenetics with their patients/clients. Methods: A survey based on the theory of planned behaviour (TPB; attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioural control) was developed and sent by email to RD members of the Ordre professionnel des diététistes du Québec. Multiple regression analyses were performed to examine the determinants of intention and behaviour. Results: A total of 141 RDs completed the questionnaire (5.8% response rate). On a scale from −2 to 2 (from strongly disagree to strongly agree), the intention of discussing nutrigenetics with patients/clients was neutral (mean of −0.07 ± 0.92). The TPB construct of attitude was the most strongly associated with intention (β = 0.66, P < 0.0001) followed by perceived behavioural control (β = 0.33, P < 0.0001) and subjective norm (β = 0.21, P = 0.03). Finally, 13 out of 141 RDs (~9%) actually practiced the behaviour, which was to have discussed nutrigenetics with their patients/clients in the last 3 months. Only perceived behavioural control contributed to explain the behaviour (β = 0.17, P < 0.0001). Conclusions: Main determinants of the intention of RDs to discuss nutrigenetics with their patients/clients were determined. This knowledge will help inform the design of future educational content about nutrigenetics.
Purpose: Peer education (PE) has been used effectively in nutrition; however, research examining dietitians’ attitudes regarding PE is lacking. Methods: An online survey was sent to a random sample of 1198 Dietitians of Canada members to assess attitudes regarding PE by practice area. Results: A representative sample of dietitians by practice area and location was obtained (n = 229; 19%). Their total attitude score (TAS) was 226 ± 26 (mean ± SD) out of 295 (maximum). Community/public health dietitians had significantly higher TASs compared with clinical dietitians (234 ± 23 vs. 221 ± 27, respectively; P = 0.03). Dietitians believed PE to be most useful in community settings (P < 0.001), with cultural groups or adolescents (P < 0.001), and for healthy eating program goals (P < 0.001). The barrier most agreed with was limited financial resources, whereas the highest perceived benefits were social support and experience/employment for participants and peer educators, respectively. Overall, 63% agreed PE is an effective model, and 59% agreed that PE should be used more often in nutrition. Conclusions: Dietitians have a positive attitude towards PE, with community/public health dietitians having the most positive attitudes. Dietitians believe PE is useful with specific target populations and particular program goals/strategies; however, they could be challenged to consider PE in a greater variety of programs.
Purpose: This qualitative study, guided by a phenomenological approach, explored senior-level undergraduate, nutrition students’ perceptions of how obesity and weight bias were addressed in the undergraduate curricula and how the curricula influenced their attitudes toward individuals with obesity. Methods: Twenty senior-level undergraduate, nutrition students from the University of Guelph participated in interviews. Interviews were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. Thematic analysis entailed open, axial, and selective coding. Results: Participants’ sources of information about obesity in the curricula included nutrition courses, case studies, and non-nutrition courses. Regarding sources of information about weight bias in the curricula, they discussed nutrition courses, non-nutrition courses, and limited coverage of weight bias. Themes for curricular influence on attitudes toward people with obesity were increased knowledge of obesity, understanding the complexity of obesity, increased empathy toward individuals with obesity, and better ability to avoid stereotypes toward people with obesity. Conclusions: The perceptions among nutrition students varied regarding the amount and type of obesity and weight-bias information in the curricula, as well as the influence of the curricula on attitudes toward individuals with obesity, suggesting that obesity and weight bias warrant more coordinated coverage in the nutrition curricula.
Purpose: To explore strategies for disseminating online information about vitamin D to young adults. Methods: Participants were 50 males and females aged 18–25 years, living in Ontario, Canada. Eight focus groups (4 male; 4 female) were conducted; participants also completed a socio-demographic questionnaire. Audio files were transcribed verbatim; thematic analysis was used to identify key themes. Results: Thematic analysis revealed that an effective educational intervention geared towards this population should be simple, brief, interesting, personally relevant, credible, and include incentives. Conclusions: Feedback regarding intervention methodology could be used to inform interventions aiming to increase intake of vitamin D or other nutrients among young adults.
Perspectives in Practice
Poor eating habits among children are associated with negative health outcomes. The objective of this study was to use pulse/soy consumption as an indicator to evaluate the eating profile of young Manitobans. Data from the Canadian Community Health Survey Cycle 2.2 were used for analysis and restricted to Manitoba residents aged 2 to 18 years (n = 1840). Consumers were identified as individuals who reported eating at least 1 pulse/soy product during their recall. On any given day, 8.2% of Manitobans reported consumption of pulses/soy. Intakes of fibre, protein, magnesium, and zinc were higher in consumers only when expressed relative to total caloric intake. Consumers also reported increased intakes of meat and alternatives. Total intakes of vitamin D, fibre, and fruit and vegetable consumption were low among all groups. Sodium intakes in both groups were high when compared with levels recommended by health professionals. These results indicate that there are many dietary issues affecting Manitoba children, suggesting the need for more research targeting dietary habits of children and youth, the quality of the food supply, and effective strategies in nutrition education.
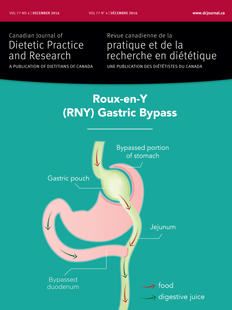
We explored differences in dietary behaviours, energy, and macronutrient intake among individuals who had regained or maintained weight loss 5 or more years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). This study assessed 27 adults who underwent RYGB an average of 12.1 ± 3.7 years before this study was conducted. Dietary assessment was performed using 3-day food records. Daily energy intake (kcal), protein (g), carbohydrate (g), fat (g), and alcohol intake (g) were computed using the ESHA’s Food Processor®. Participants were classified by percent weight loss, maintainers (≥38 %), and regainers (≤30 %). Daily carbohydrate consumption was greater in regainers (222 ± 84.3 g) compared with maintainers (162 ± 67.5 g), (P < 0.05). Thirty-seven percent of participants were not consuming the recommended amount of protein and 26% reported never taking vitamin supplements after surgery. Alcohol consumption was higher among regainers (18.5 ± 30.9 g) compared with maintainers (2.6 ± 6.5 g), (P < 0.05). Finally, 74% of the participants reported no contact with a Registered Dietitian, whereas 78 % were in contact with a health care professional once a year post-surgery. Differences were seen in carbohydrate intake and alcohol consumption between weight maintainers and regainers. These data suggest dietitians need to play a more active role in the long-term care of this medically complex population.
Report
Purpose: Patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) often experience low bone mineral density (BMD) pre- and post-lung transplantation (LTX). The study purpose was to describe BMD and micronutrient status in adults with CF pre- and post-LTX. Methods: Twelve patients with CF (29 ± 8 years) were recruited from the CF clinic at the University of Alberta Lung Transplant Program. BMD and vitamins A, D, E, K status, and parathyroid hormone were measured pre- and post-LTX. Results: No significant differences pre- and post-LTX were observed at the different bone sites measured (lumber–spine, femoral–neck (FN), hip, and femoral–trochlea) (P > 0.05). BMD T-scores (<−2) was present in lumbar–spine, FN, hip, and femoral–trochlea in 33%, 17%, 17%, and 25% of individuals pre-LTX and 58%, 33%, 58%, and 33% of individuals post-LTX, respectively. More than 50% of patients had suboptimal vitamin K levels (PIVKA-II values >3 ng/mL) pre- and post-LTX. Conclusion: Adults with CF pre- and post-LTX had reduced BMD and suboptimal vitamin K status.
Purpose: To understand how and where parents of infants and young children (children ≤5 years old) prefer to receive nutrition information. Methods: A 1-page survey was developed and pilot tested at 2 community agencies. The final survey was distributed at 18 community health centres (CHCs) in Calgary and surrounding rural areas. Any parent attending a well-child visit (child ≤5 years old) was able to participate. Results: Five hundred and twenty-nine surveys were completed. The majority of respondents at every CHC identified online reading (79.2%) in their home (86.0%) as the preferred method and location to receive nutrition information. Almost all (99.4%) participants had internet access. Handouts (38.6%) were the second most popular way to receive nutrition information. In-person and online classes were only a preferred method by a small percentage of respondents, 10.6% and 8.1%, respectively. Conclusions: Appropriate, evidence-based nutrition websites should be promoted to parents with young children. Health professionals should be aware that parents likely access nutrition information online, and they need to provide an opportunity for parents to discuss what they found. Future research is needed to understand which websites parents access for online nutrition information and how they discern whether it is credible.
Purpose: This study reports on the effect of a group-based nutrition and physical activity intervention program on nutrition knowledge and eating habits in a cohort of people with obesity. Methods: A quasi-experimental design with pre- and post-test measures. The intervention consisted of physical activity led by certified exercise physiologists and a nutritional education component led by registered dietitians over a 6-month period followed by 6 months of self-management. Participants’ nutrition knowledge and eating habits were assessed using the modified Nutrition Assessment, the Nutrition Knowledge Survey, and the Food Choice Questionnaires at baseline, after the 6-month intervention, and after 6 months of self-management. Results: Complete data were available for 59 (40%) of participants after 12 months because of attrition. Nutritional knowledge and behaviours improved. Participants reported increasing their consumption of healthy foods during the active intervention and maintained these changes through the self-management phase. Knowledge of healthy foods was improved and a greater likelihood of choosing food for weight control and health properties was reported. Conclusions: Knowledge and reported consumption of healthier nutrition improved during the active intervention and was maintained during the self-management period for individuals who completed the program. Registered dietitians can play an important role in managing patients with obesity in group settings.